Sleep Disturbances as a Risk Factor for Stroke
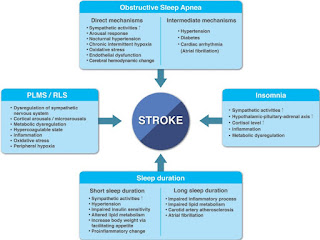
Sleep is an indispensable part of life, as with feeding and reproduction, all animal species require sleep. Humans sleep almost one-thirds of their lifetime,which is similar in industrialized and in pre-industrial societies. Sleep, although characterized by quiescence and diminished responsiveness, is not a simple state of rest, but rather a cyclic state of periodic transitions between rapid-eye-movement (REM) and non-REM (NREM) sleep, which are precisely regulated by the central nervous system. Along with the brain and other organs or physiological streams, the cardiovascular system achieves homeostatic restoration during sleep, mainly through autonomic circulatory control. For example, the decrease in blood pressure during sleep, “dipping,” is a key biomarker of cardiovascular health, secondary to changes in activity and posture and also under the influence of sleep and circadian rhythms. During NREM sleep, the largest portion (up to 80%) of normal adult sleep, the autono...

